Build your own image gallery CMS
Learn how to create a custom image gallery CMS using Xata, Astro, and Cloudflare Pages.
Written by
Rishi Raj Jain
Published on
January 4, 2024
In this post, you'll create an image gallery CMS using Astro, Xata, and Cloudflare Pages. You'll learn how to:
- Set up Xata
- Create a schema with different column types
- Resize and blur images
- Fetch all records without pagination
- Handle forms in Astro using view transitions
You'll need the following:
- A Xata account
- Node.js 18 or later
- A Cloudflare account
| Technology | Description |
|---|---|
| Xata | Serverless database platform for scalable, real-time applications. |
| Astro | Framework for building fast, modern websites with serverless backend support. |
| Tailwind CSS | CSS framework for building custom designs |
| Cloudflare Pages | Platform for deploying and hosting web apps with global distribution. |
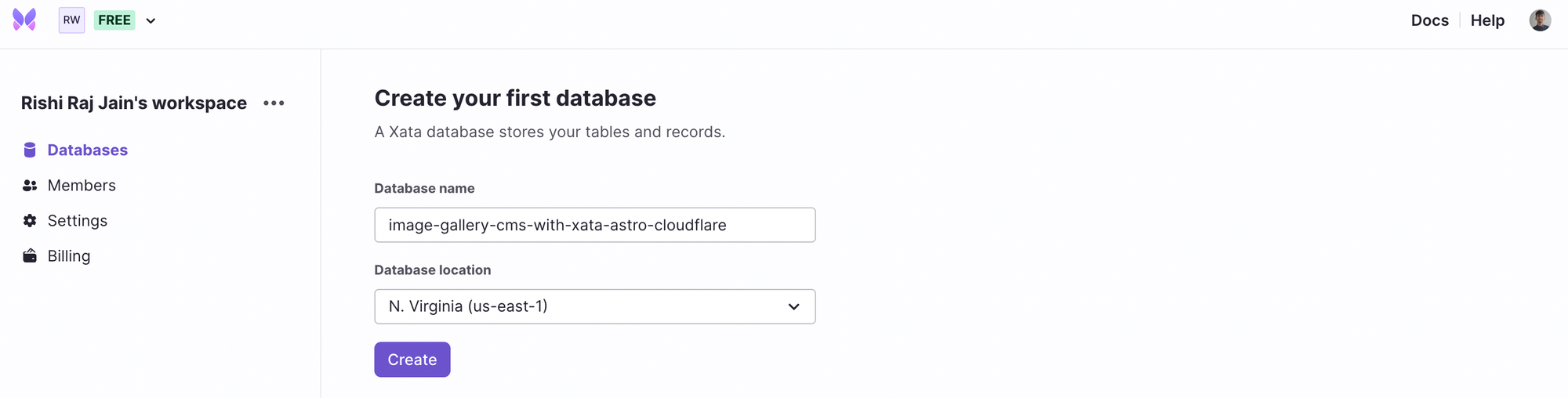
After you've created a Xata account and are logged in, create a database.
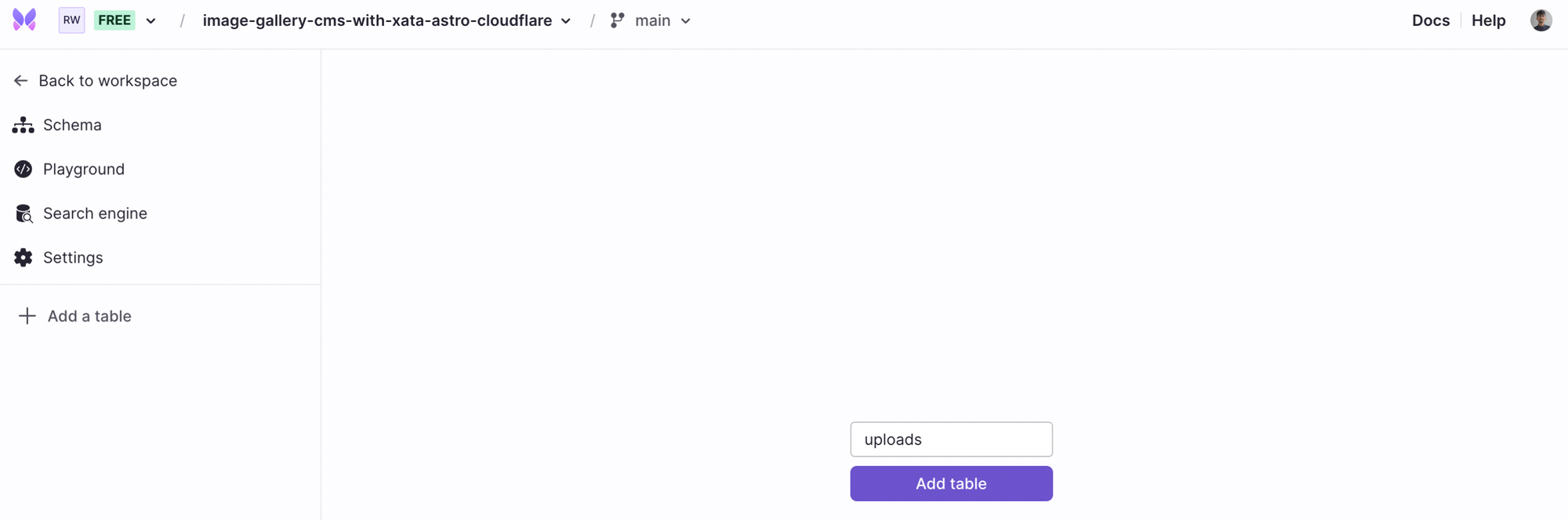
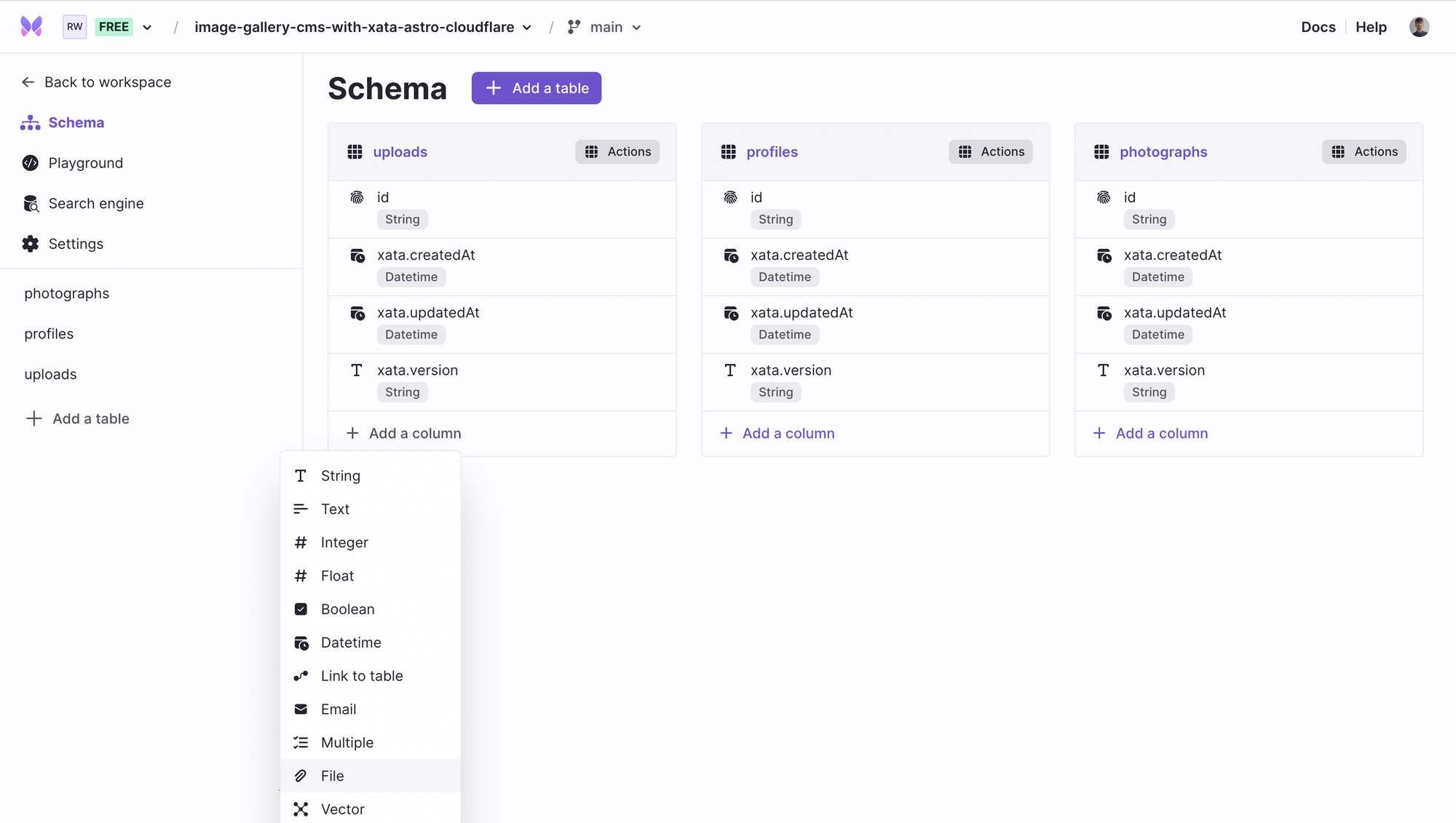
The next step is to create a table, in this instance uploads, that contains all the uploaded images.
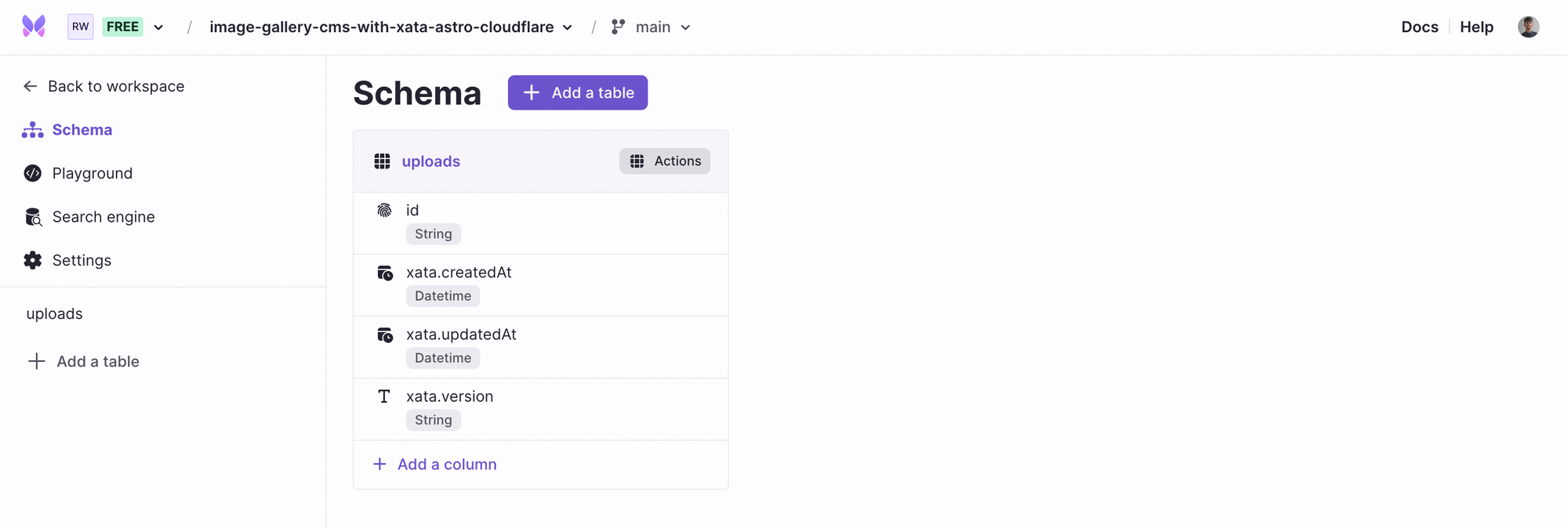
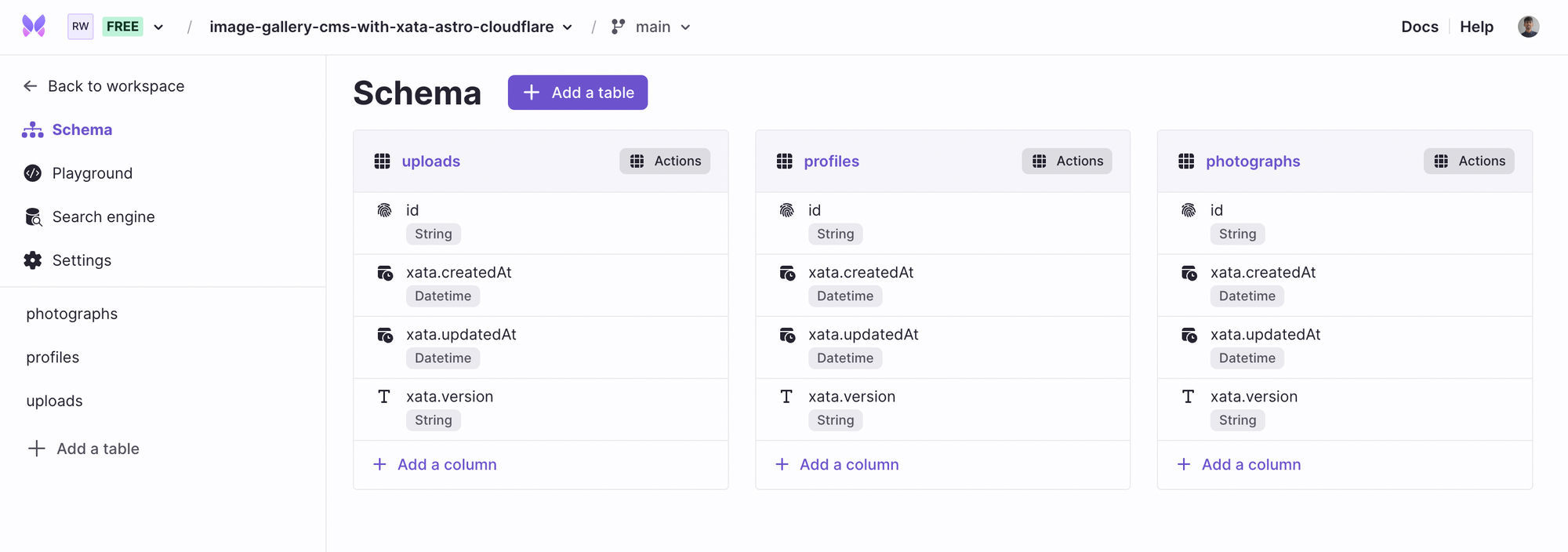
Great! Now, click Schema in the left sidebar and create two more tables profiles and photographs. You can do this by clicking Add a table. The newly created tables will contain user profile data and user uploaded photograph(s) data respectively.
With that completed, you will see the schema.
Let’s move on to adding relevant columns in the tables you've just created.
In the uploads table, you want to store all the images only (and no other attributes) so that you can create references to the same image object again, if needed.
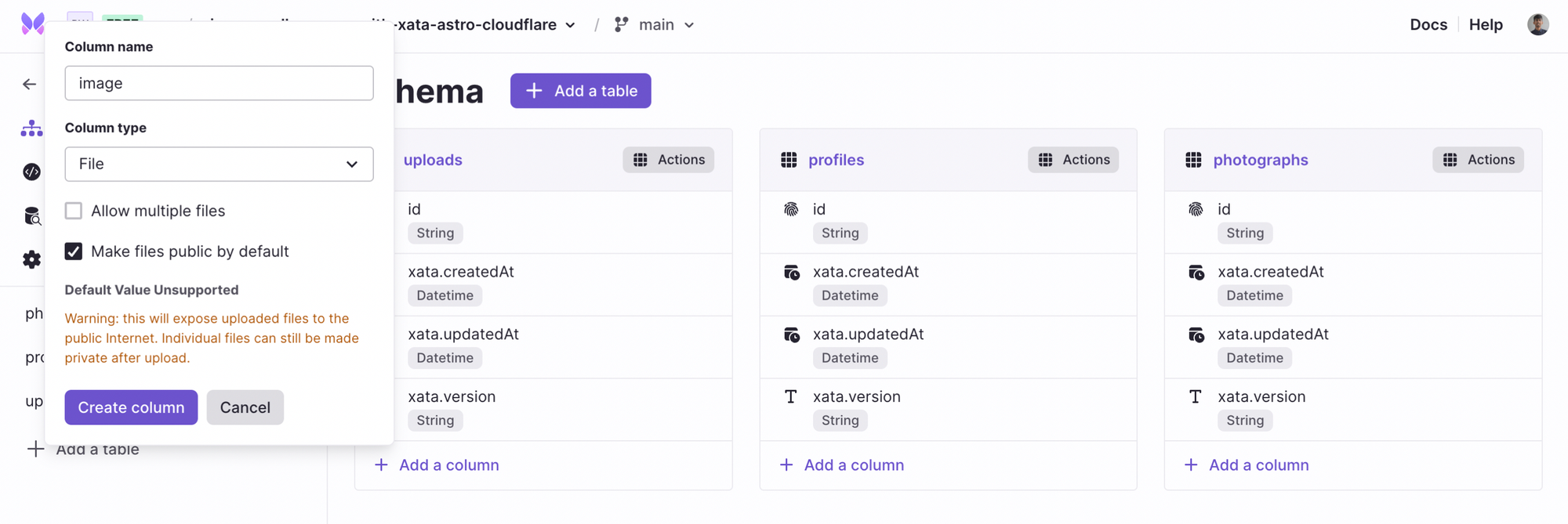
Proceed with adding the column named image. This column is responsible for storing the file type objects. In our case, the file type object is for images, but you can use this for storing any kind of blob (e.g. PDF, fonts, etc.) that’s sized up to 1 GB.
First, click + Add column and select File.
Set the column name to image and to make files public (so that they can be shown to users when they visit the image gallery), check the Make files public by default option.
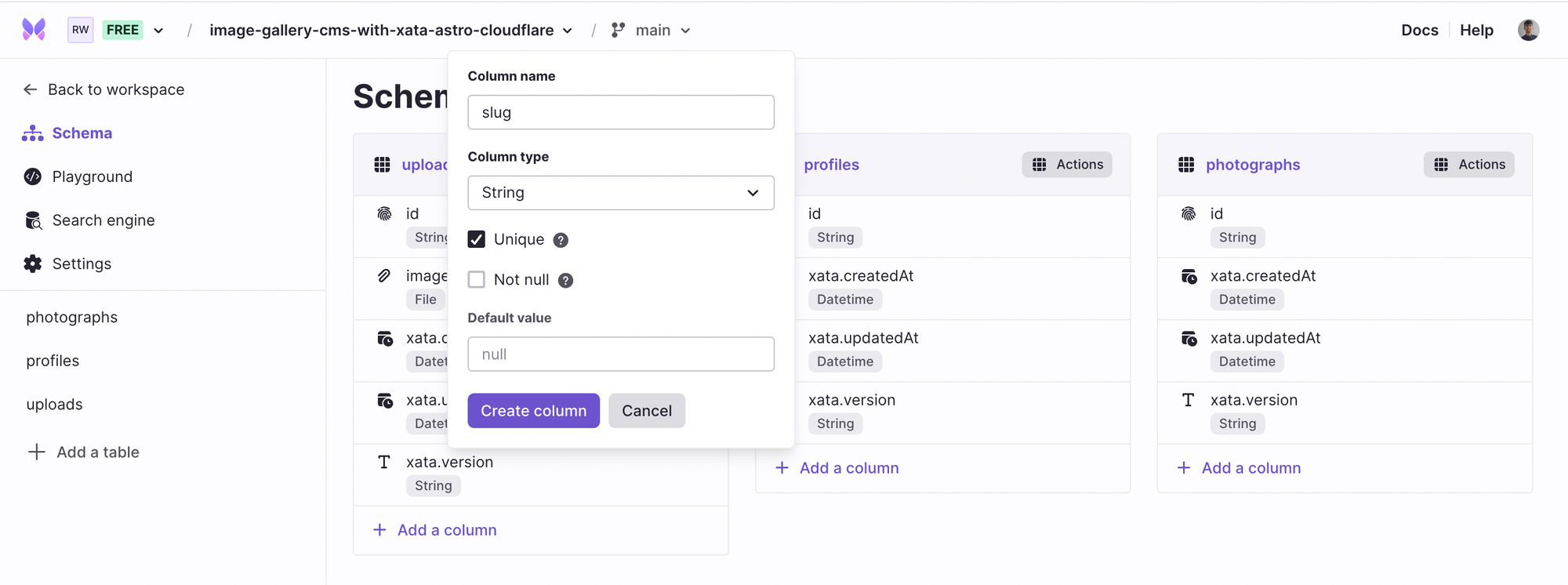
In the profiles table, we want to store the attributes such as user’s unique slug (the path of the url where gallery will be displayed of that user), their name, their image with it’s dimension, and it’s transformed image’s base64 hash. You’ll reap the benefits of storing the hash to create literally 0 Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) page(s).
Proceed with adding the column named slug. It is responsible for maintaining the uniqueness of each profile that gets created. Click + Add a column, select String type and enter the column name as slug. To associate a slug with only one user, check the Unique attribute to make sure that duplicate entries do not get inserted.
In similar fashion, create name, image, height and width columns as String type (but not Unique).
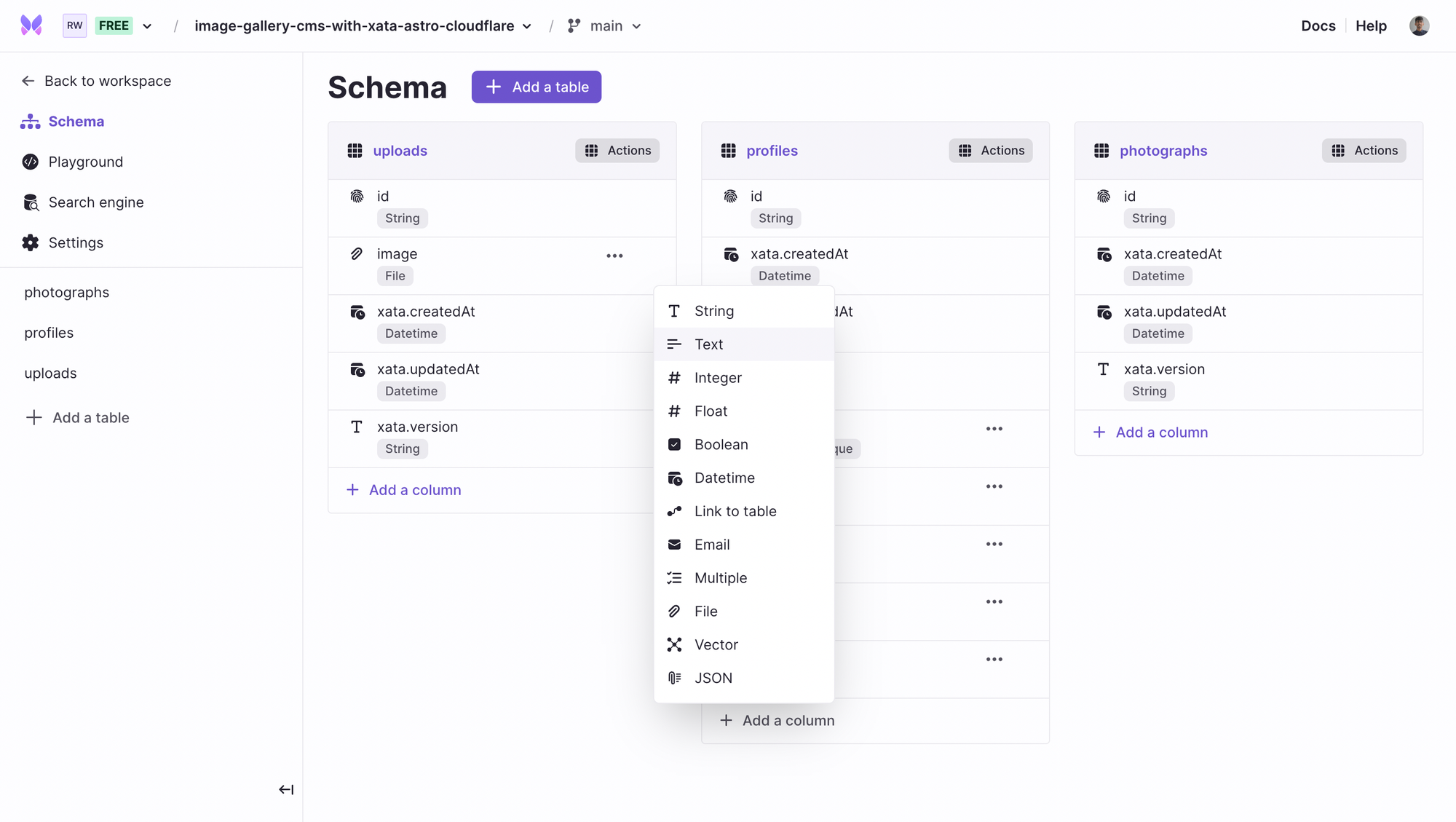
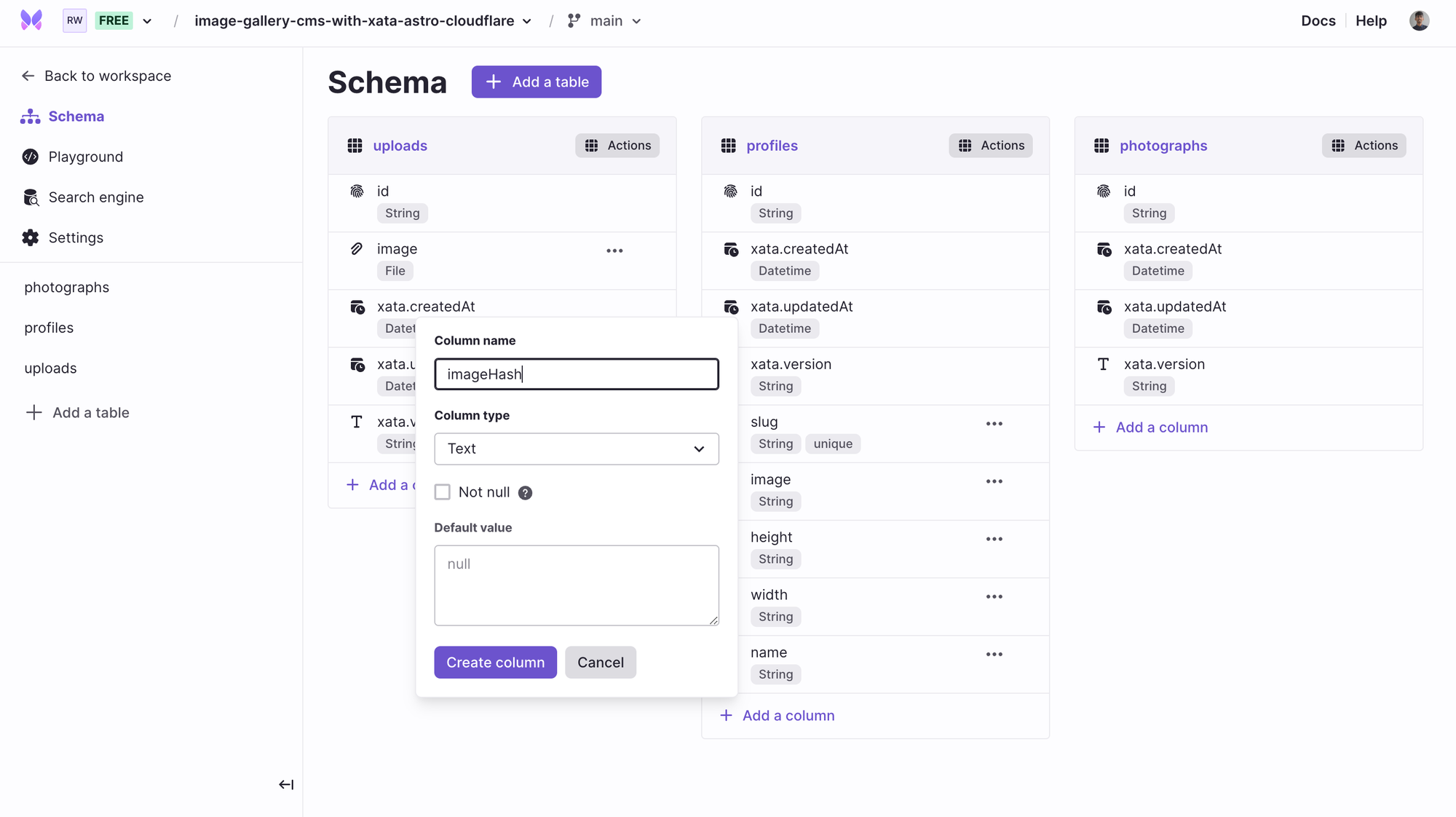
Great, you can also store imageHash as Text type so that you can instantly retrieve the image’s blur hash sized up to 200 KB. While String is a great default type, storing more than 2048 characters would require you to switch to the Text type. Read more about the limits in Xata Column limits.
Click + Add a column and select the Text type.
Enter the column name as imageHash and press Create column.
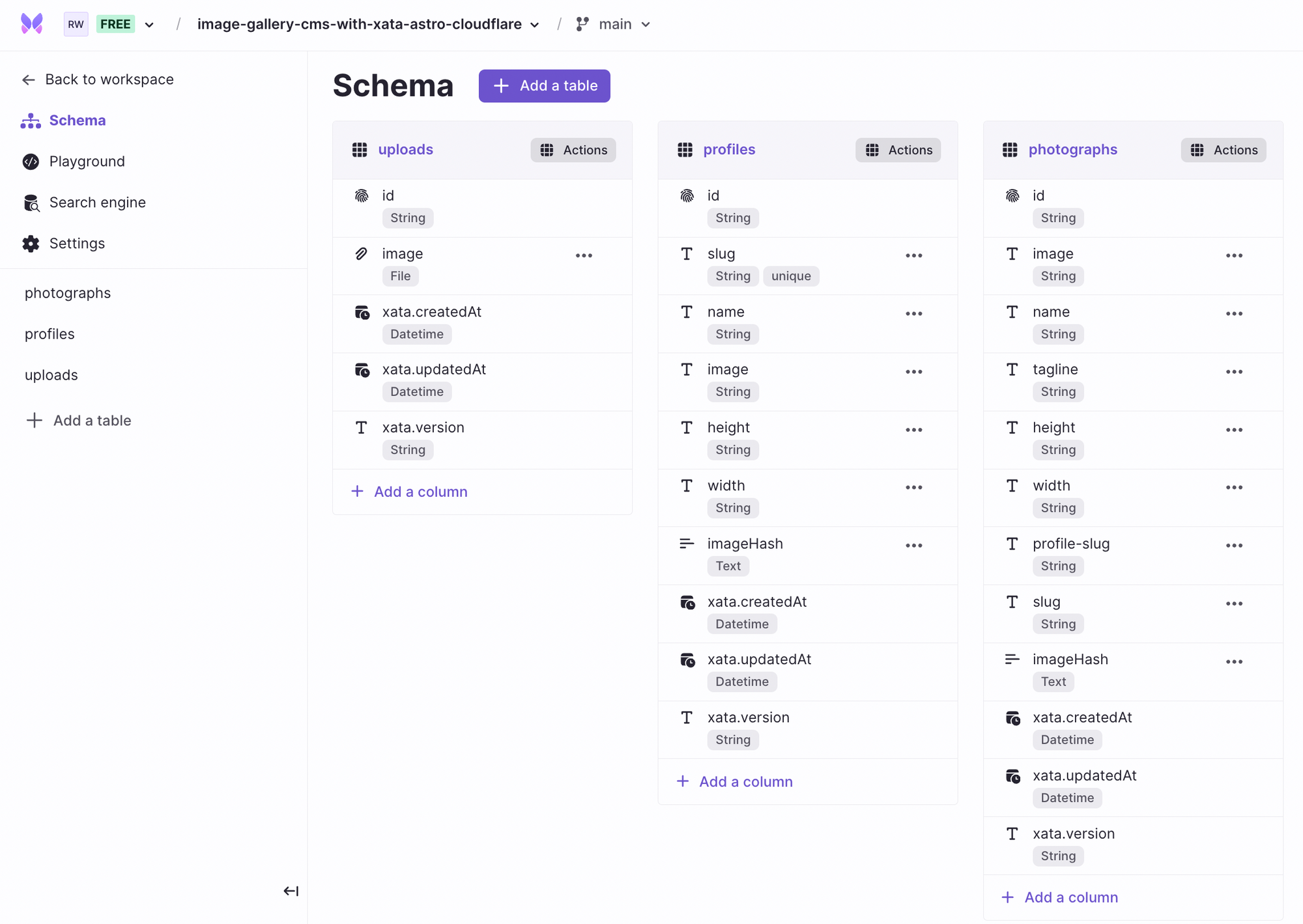
Much similar what we did above, in the photographs table, we create name, tagline, image, height, width, profile-slug, and slug as String type and imageHash as the Text type column. The columns slug and profile-slug refer to photograph’s and user profile’s slug respectively.
Lovely! With all that done, the final schema will look something like the following...
Clone the app repository and follow this tutorial; you can fork the project by running the following command:
git clone https://github.com/rishi-raj-jain/image-gallery-cms-with-astro-xata-cloudflare
cd image-gallery-cms-with-astro-xata-cloudflare
pnpm installTo seamlessly use Xata with Astro, install the Xata CLI globally:
npm install @xata.io/cli -gThen, authorize the Xata CLI so it is associated with the logged in account:
xata auth loginGreat! Now, initialize your project locally with the Xata CLI command:
xata init --db https://Rishi-Raj-Jain-s-workspace-80514q.ap-southeast-2.xata.sh/db/image-gallery-cms-with-xata-astro-cloudflareAnswer some quick one-time questions from the CLI to integrate with Astro.
You can also allow transitions on form submissions by adding the ViewTransitions component.
Here’s an example of the enabled form actions with view transitions in src/layouts/Layout.astro:
---
// File: src/layouts/Layout.astro
import { ViewTransitions } from "astro:transitions";
---
<html>
<head>
<ViewTransitions />
<!-- stuff here -->
</head>
<body>
<!-- stuff here -->
</body>
</html>This allows you to colocate the backend and frontend flow for a given page in Astro. Say, you accept a form submission containing the name, slug, and the image URL of the user, process it on the server to generate a blur Base64 hash, and sync it with your Xata serverless database. Here’s how you’d do all of that in a single Astro route (src/pages/profile/create.astro).
---
// File: src/pages/profile/create.astro
const response = { form: false, message: '', created: false, redirect: null }
// ...
if (Astro.request.method === 'POST') {
try {
// Indicate that the request is being processed
response.form = true
// Get the user email from the form submissions
const data = await Astro.request.formData()
// Get the user slug, name, and image: URL, width, and height from the form submissions
const userSlug = data.get('slug') as string
const userName = data.get('name') as string
const userImage = data.get('custom_upload_user__uploaded_image_url') as string
const userImageW = data.get('custom_upload_user__uploaded_w') as string
const userImageH = data.get('custom_upload_user__uploaded_h') as string
// Create a blur url of the user image
// Create the user record with the slug
// Redirect user to the next step
} catch (e) {
// pass
}
}
---
<form method="post" autocomplete="off">
<Upload selector="user" />
<input required name="name" type="text" placeholder="Name" />
<input
required
name="slug"
type="text"
placeholder="Slug (e.g. rishi-raj-jain)"
/>
<button type="submit">
Create Profile →
</button>
</form>As Cloudflare Pages request body size allows up to 100 MB, you’ll be able to handle image uploads on the server-side. Create an Astro endpoint (src/pages/api/upload/index.ts) to receive POST requests containing image binaries and use the Xata SDK to store them in the uploads table.
After doing sanity checks on the request body, first create a new (empty) record in your uploads table, and then use it as a reference to place the image (buffer) using the Xata TypeScript SDK. Once successfully completed, the endpoint responds with the image’s public URL, height and width back to the front-end to include in the form fields.
// File: src/pages/api/upload/index.ts
import { json } from '@/lib/response';
import { getXataClient } from '@/xata';
import type { APIContext } from 'astro';
// Import the Xata Client created by the Xata CLI in src/xata.ts
const xata = getXataClient();
export async function POST({ request }: APIContext) {
const data = await request.formData();
const file = data.get('file');
// Do sanity checks on file
try {
// Obtain the uploaded file as an ArrayBuffer
const fileBuffer = await file.arrayBuffer();
// Create an empty record in the uploads table
const record = await xata.db.uploads.create({});
// Using the id of the record, insert the file using upload method
await xata.files.upload({ table: 'uploads', record: record.id, column: 'image' }, fileBuffer, {
mediaType: file.type
});
// Read the inserted image
const { image } = await xata.db.uploads.read(record.id);
// Destructure its dimension and public URL
const { url, attributes } = image;
const { height, width } = attributes;
return json({ height, width, url }, 200);
} catch (error) {
// Handle errors
}
}Once a user submits their profile on the /profile/create page, before creating a record in the profiles table, generate a Base64 buffer of their blurred images. To create blurred images from the originals, use Xata image transformations. With Xata image transformations, you’re able to request an on-demand public URL which resizes the image to given height and width, and blur the image. In this particular example, you can resize the image to 100 x 100 dimensions and blur it up to 75% from the original.
---
// File: src/pages/profile/create.astro
// Import the Xata Client created by the Xata CLI in src/xata.ts
import { getXataClient } from '@/xata'
// Import the transformImage function by Xata Client
import { transformImage } from '@xata.io/client'
const response = { form: false, message: '', created: false, redirect: null }
// ...
if (Astro.request.method === 'POST') {
// Fetch the Xata instance
const xata = getXataClient()
// ...
// Create a blur URL of the user image
// Using Xata image transformations to obtain the image URL
// with a fixed height and width and 75% of it blurred
const userBlurURL = transformImage(userImageURL, {
blur: 75,
width: 100,
height: 100,
})
// Create a Base64 hash of the blur image URL
const userBlurHash = await createBlurHash(userBlurURL)
// Create the user record with the slug
// Redirect user to the next step
}
---After you have generated blurred images, the last step in publishing profiles (similar to what’s done in publishing photographs) is to create a user record with relevant details using the Xata TypeScript SDK’s create command. In Astro, we then set the successful message for the user before they are redirected to the photograph upload page. The integrated conditional rendering ensures a visual cue of the operation's success or failure, providing a responsive and user-friendly experience.
---
// File: src/pages/profile/create.astro
// Import the Xata Client created by Xata CLI in src/xata.ts
import { getXataClient } from '@/xata'
const response = { form: false, message: '', created: false, redirect: null }
// ...
if (Astro.request.method === 'POST') {
// ...
// Create the user record with the slug
await xata.db.profiles.create({
slug: userSlug,
name: userName,
image: userImage,
width: userImageW,
height: userImageH,
imageHash: userBlurHash,
})
// Send the user to photograph upload page
response.redirect = '/photograph/create'
// Set the relevant message for the user
response.message = 'Published profile successfully. Redirecting you to upload your first photograph...'
}
---
<!-- Render conditional states using the onboarded flag -->
{
response.form &&
(response.created ? (
<p class="rounded bg-green-100 px-3 py-1">{response.message}</p>
) : (
<p class="rounded bg-red-100 px-3 py-1">{response.message}</p>
))
}
<!-- Profile Form -->
<!-- Redirect user to the next location -->
<script define:vars={{ success: response.created, location: response.redirect }}>
if (success) {
setTimeout(() => {
window.location.href = location
}, 1000)
}
</script>The user profile page (src/pages/[profile]/index.astro) leverages the Xata Client to dynamically fetch and display all the photographs (not paginated) for a specific user profile. To engage users visually as soon as they open the gallery, we use the stored imageHash value as the background of the images (to be loaded). To prevent CLS, we use the stored width and height values to inform the browser of the expected dimensions of the images.
---
// File: src/pages/[profile]/index.astro
// Import the Xata Client created by Xata CLI in src/xata.ts
import { getXataClient } from '@/xata'
import Layout from '@/layouts/Layout.astro'
// Get the profile slug from url path
const { profile } = Astro.params
// Fetch the Xata instance
const xata = getXataClient()
// Get all the photographs related to the profile
const profilePhotographs = await xata.db.photographs
// Filter the results to the specific profile
.filter({ 'profile-slug': profile })
// Get all the photographs
.getAll()
---
<Layout className="flex flex-col">
<div class="columns-1 gap-0 md:columns-2 lg:columns-3">
{
profilePhotographs.map(
({ width: photoW, height: photoH, name: photoName, image: photoImageURL, tagline: photoTagline, imageHash: photoImageHash }, _) => (
{/* Destructure the width and height to prevent CLS */}
<img
width={photoW}
height={photoH}
alt={photoName}
src={photoImageURL}
{/* Do not lazy load the first image that's loaded into the DOM */}
loading={_ === 0 ? 'eager' : 'lazy'}
class="transform bg-cover bg-center bg-no-repeat will-change-auto"
{/* Create a blur effect with the imageHash stored */}
style={`background-image: url(${photoImageHash}); transform: translate3d(0px, 0px, 0px);`}
/>
),
)
}
</div>
</Layout>The repository is ready to deploy to Cloudflare. Follow the steps below to deploy seamlessly with Cloudflare 👇🏻
- Create a GitHub repository with the app code.
- Click Create application in the Workers & Pages section of Cloudflare dashboard.
- Navigate to the Pages tab and select Connect to Git.
- Link the created GitHub repository as your new project.
- Scroll down and update the Framework preset to Astro.
- Update the environment variables from the
.envlocally. - Click Save and Deploy and go back to the project Settings > Functions.
- Add
nodejs_compatto the Compatibility flags section - Deploy! 🚀
Cloudflare Pages stood out for this particular use case as it offers up to 100 MB request body size in their Free plan. This helped to bypass the 4.5MB request body size limit in various serverless hosting providers.
For more detailed insights, explore the references cited in this post.
| Resource | Link |
|---|---|
| Demo Image Gallery | Demo |
| GitHub Repo | Repository |
| Astro with Xata | Getting Started Guide |
| Astro View Transition Forms | Astro Transitions |
| Xata File Attachments | Xata File APIs |
| Xata Transformations | Xata Image Transformations |
| Xata Get Records | Xata Querying |
| Cloudflare Workers Limits | Cloudflare Limits |
We'd love to hear from you if you have any feedback on this tutorial, would like to know more about Xata, or if you'd like to contribute a community blog or tutorial. Reach out to us on Discord or join us on X | Twitter. Happy building 🦋
Start free,
pay as you grow
Xata provides the best free plan in the industry. It is production ready by default and doesn't pause or cool-down. Take your time to build your business and upgrade when you're ready to scale.
- Single team member
- 10 database branches
- High availability
- 15 GB data storage
- Single team member
- 10 database branches
- High availability
- 15 GB data storage
Copyright © 2025 Xatabase Inc.
All rights reserved.